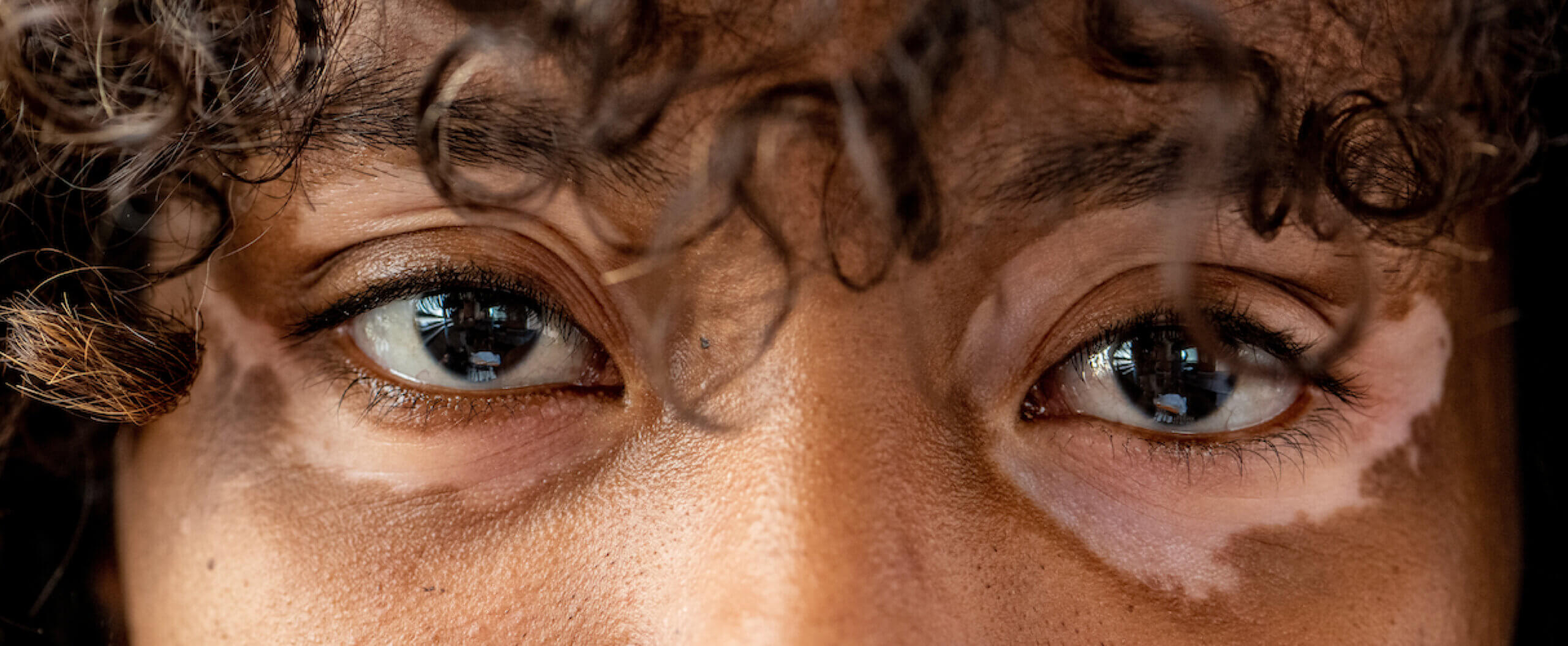
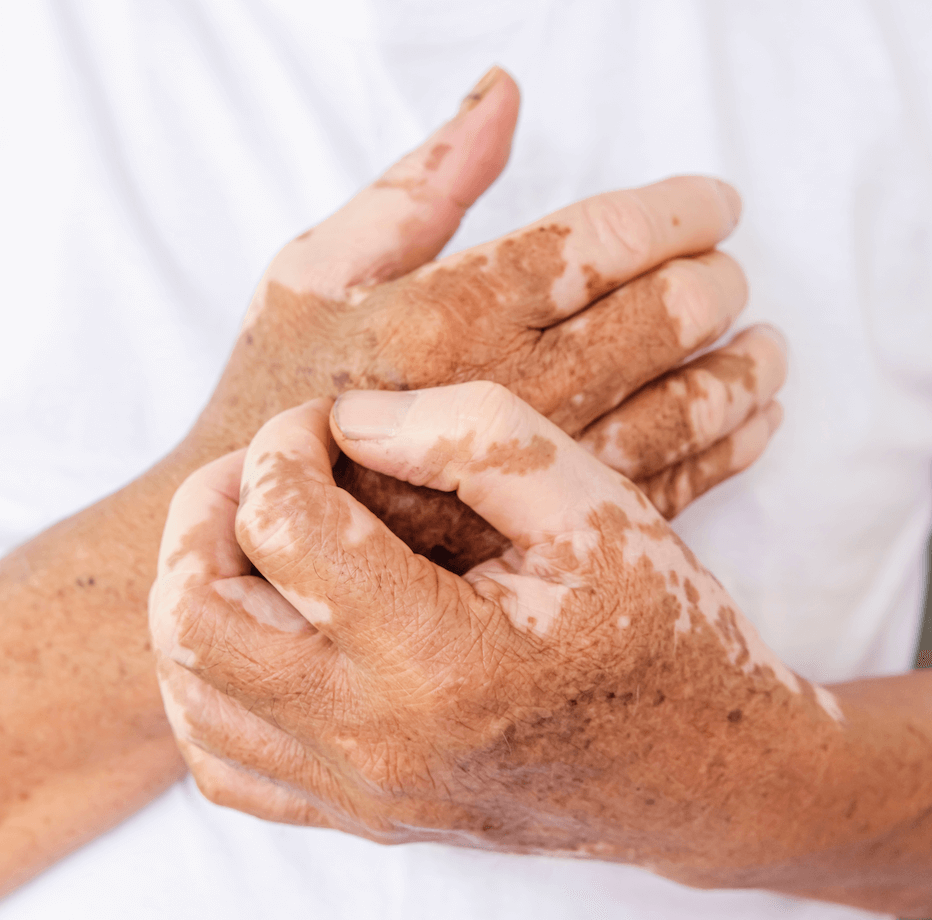
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic skin disease that makes patches of skin lose their natural pigment.
Vitiligo is a chronic skin disease that makes patches of skin lose their natural pigment. When there is a deficiency in melanocytes (pigment-producing cells), the skin turns a pale white colour. An absence of melanocytes can happen anywhere on the body, including the scalp and inside the mouth.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disease that causes your body to attack your healthy skin cells that produce melanin and skin colour. Patients can rest assured knowing that despite its appearance, it is not life-threatening or contagious. Vitiligo can occur at any age, but it usually forms before the age of 20.
While the exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, this condition develops when the immune system destroys cells called melanocytes, which are responsible for producing skin pigmentation. Vitiligo may develop at any age. Your chances of having vitiligo are increased if you have a family member with the condition, or if you have an autoimmune condition, such as a thyroid disease called Hashimoto’s disease or a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
Our dermatologists may recommend phototherapy, laser treatment, or topical medications to restore pigmentation to the skin. Topical medications and light therapies may be prescribed together for best results. Topical medications for vitiligo may minimize the appearance of depigmented spots on the skin.
Although vitiligo is not contagious or life-threatening, it can negatively affect your confidence and self-esteem. There is no cure for this condition, and there’s no way to fully avoid the resulting continual loss of pigment, but there are treatments that can help to restore a more uniform skin colour.

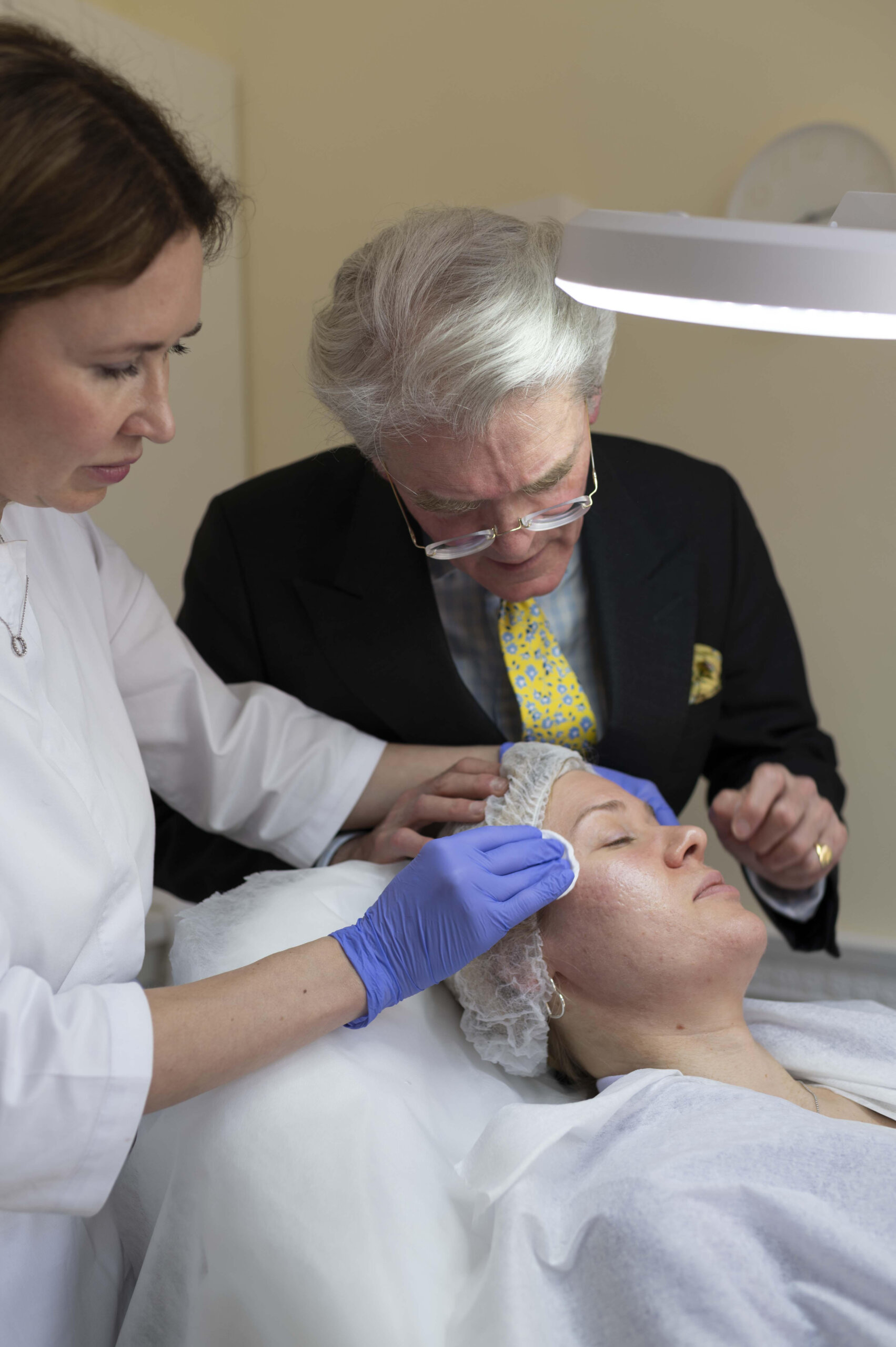
Consultation
- Detailed history of your skin concern
- Total skin examination
- Holistic assessment of your health
- Diagnosis
- Discussion of treatment options
- Personalised treatment plan
- Treatment
FAQs
Vitiligo is progressive, but there’s no way to know how quickly your vitiligo will spread or how much skin pigmentation you’ll lose.
Non-segmental vitiligo tends to develop slowly. People may develop new patches of depigmented skin on and off throughout their lives.
Segmental vitiligo tends to advance more quickly than non-segmental at first, causing rapid depigmentation during the first 6 months to a year.
You likely won’t continue to lose skin colour indefinitely in this type of vitiligo, however. After a period of rapid loss, depigmentation stabilizes, and you may never develop new patches.
See answer

There’s currently no cure for vitiligo. But treatments are available that can help restore skin color and slow depigmentation — though results vary
See answer

Vitiligo can be progressive, but it’s an unpredictable condition.
You may experience noticeable, advancing depigmentation or slow changes over a long period of time. Some types of vitiligo eventually stabilise.
Larger patches may continue to broaden and spread, although they often remain in the same location for years. If you developed this condition early in life, there’s a higher chance that more of your body will eventually be affected and your rate of vitiligo progression will be faster compared with people who develop it later in life.
See answer



