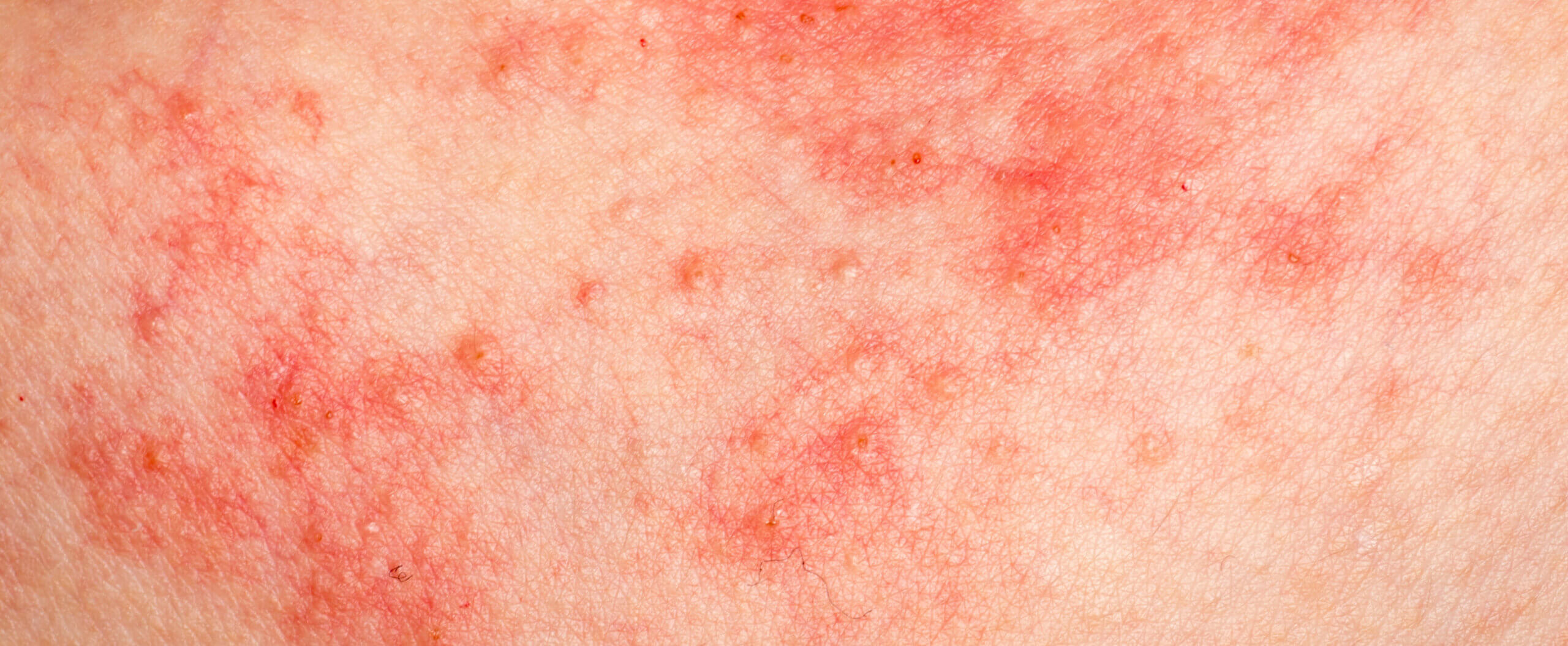
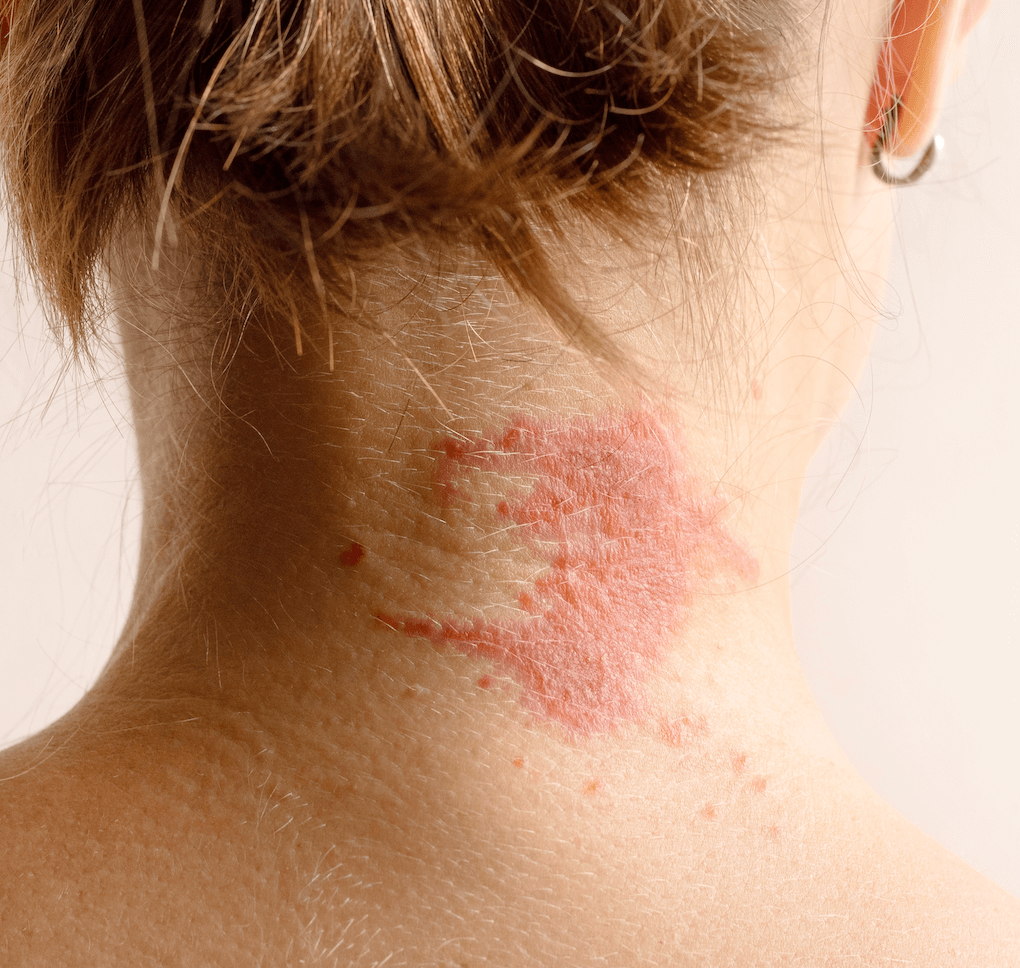
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes.
It is a type of eczema. It’s the formation of an itchy, dry rash on the skin that is often irritated due to inflammation. Patients tend to have eczema occur on the neck, wrists, knees, or elbows, but these patches of itchy skin can occur anywhere on the body. Atopic dermatitis has a cycle that begins with the release of inflammatory chemicals. After the release of these chemicals, you will naturally react to an itch by scratching it. Due to scratching your itch, you damage your skin further, which results in even more inflammatory chemicals being released. This process results in the intense itching of eczema.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
– Intense itching (can be worse at night)
– Small, raised bumps on the skin
– Raw, swollen, or inflamed skin
– Dry, cracking, textured skin
– Red, pink, or brown patches of skin
Atopic dermatitis treatment options include oral medications, topical creams, and light therapy. At Devonshire Dermatology, our dermatologists can help choose the best treatment for you depending on the severity of your case and any previous eczema treatments you may have undergone.
Oral medications such as steroids may be suggested if your case of eczema is severe or does not respond to topical eczema treatments. Topical agents such as a hydrocortisone cream or ointment may be prescribed for a milder case of eczema. If you are suffering from a more severe case of atopic dermatitis and hydrocortisone cream is not helping, a prescription-strength steroid cream may be prescribed to help ease the discomfort of eczema. Eczema can also be managed using antihistamine creams or ointments, which can help soothe and treat the irritated and inflamed skin on and surrounding an eczema outbreak.
Consultation
- Detailed history of your skin concern
- Total skin examination
- Holistic assessment of your health
- Diagnosis
- Discussion of treatment options
- Personalised treatment plan
- Treatment
FAQs
Dermatitis is a general term for common skin irritation and inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis, also called eczema, is a long-term type of dermatitis that usually runs in families. It causes a patchy rash that makes your skin itchy, red, scaly, and dry.
See answer

Many things can trigger your atopic dermatitis or make it worse:
-
Stress
-
Changes in temperature or humidity
-
Skin infections from bacteria
-
Dust mites, molds, and dander
-
Some kinds of makeup
-
Clothes that rub on your skin, especially wool
-
For babies, sometimes food allergies
See answer

The symptoms of eczema are different for babies compared to children and adults.
For babies with eczema, the rash:
-
Is red, oozing, crusty, and itchy
-
Starts on the face and spreads to their neck, scalp, hands, arms, feet, and legs
-
Can cover large areas of their bodies
-
May last for several months before improving
For children and adults with eczema, the rash:
-
Itches a lot
-
Usually shows up in only one or a few spots, especially your hands, upper arms, in front of your elbows, behind your knees or around your eye
-
Can flare up again and again, usually in the same places
See answer

Doctors can diagnose atopic dermatitis by looking at the rash and asking you about your personal and family health history.
See answer

Doctors can’t cure eczema, but to help with your symptoms, they may suggest that you:
-
Apply medicines, such as corticosteroid and other creams, to lessen itching and heal your skin
-
Keep your skin moist with cool water compresses, lotions, petroleum jelly, or vegetable oil after baths or showers
-
Take a bath or shower only once a day to keep your skin from getting dry
-
Take a bath in water with a small amount of bleach, colloidal oatmeal (a product made of finely ground oatmeal), or tar medicine
-
Blot your skin dry after a bath or shower instead of rubbing it dry
If your eczema is severe, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroid pills or other medicines that slow down your immune system.
See answer

To help prevent eczema from getting worse:
-
Avoid scratching
-
Use moisturizers to keep your skin from getting dry
-
Avoid things that irritate your skin
-
Avoid foods that you’re allergic to
-
Avoid sweating and very hot or cold temperatures
-
Wear light cotton clothes and avoid wool and other rough fabrics
-
Use a humidifier in the house to keep the air moist
-
Try to lower your emotional stress
See answer